文献:Elucidating Driving Forces for Liposome Rupture: External Perturbations and Chemical Affinity
文献链接:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/la300127m
作者:Xi WangMatthew M. ShindelSzu-Wen WangRegina Ragan
摘要:
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) studies under aqueous buffer probed the role of chemical affinity between liposomes, consisting of large unilamellar vesicles, and substrate surfaces in driving vesicle rupture and tethered lipid bilayer membrane (tLBM) formation on Au surfaces. 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-poly(ethylene glycol)-2000-N-[3-(2-pyridyldithio) propionate] (DSPE-PEG-PDP) was added to 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (POPC) vesicles to promote interactions via Au–thiolate bond formation. Forces induced by an AFM tip leading to vesicle rupture on Au were quantified as a function of DSPE-PEG-PDP composition with and without osmotic pressure. The critical forces needed to initiate rupture of vesicles with 2.5, 5, and 10 mol % DSPE-PEG-PDP are approximately 1.1, 0.8, and 0.5 nN, respectively. The critical force needed for tLBM formation decreases from 1.1 nN (without osmotic pressure) to 0.6 nN (with an osmotic pressure due to 5 mM of CaCl2) for vesicles having 2.5 mol % DSPE-PEG-PDP. Forces as high as 5 nN did not lead to LBM formation from pure POPC vesicles on Au. DSPE-PEG-PDP appears to be important to anchor and deform vesicles on Au surfaces. This study demonstrates how functional lipids can be used to tune vesicle–surface interactions and elucidates the role of vesicle–substrate interactions in vesicle rupture.
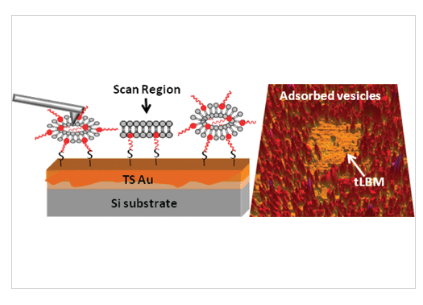
在水性缓冲液下进行的原子力显微镜(AFM)研究探讨了由大型单层囊泡组成的脂质体与基底表面之间的化学亲和力在驱动囊泡破裂和Au表面形成栓系脂质双层膜(tLBM)中的作用。
将1,2-二硬脂酰-sn-甘油-3-磷酸乙醇胺-N-聚(乙二醇)-2000-N-[3-(2-吡啶基二硫代)丙酸酯](DSPE-PEG-PDP)加入1-棕榈酰-2-油酰基-sn-甘油3-磷酸胆碱(POPC)囊泡中,以促进通过金-硫醇键形成的相互作用。在有和没有渗透压的情况下,AFM尖端引起的导致Au上囊泡破裂的力被量化为DSPE-PEG-PDP成分的函数。
引发2.5、5和10 mol%DSPE-PEG-PDP囊泡破裂所需的临界力分别约为1.1、0.8和0.5 nN。对于具有2.5mol%DSPE-PEG-PDP的囊泡,tLBM形成所需的临界力从1.1nN(无渗透压)降低到0.6nN(有5mM CaCl2的渗透压)。
高达5nN的力不会导致Au上纯POPC囊泡形成LBM。DSPE-PEG-PDP似乎对Au表面上的囊泡锚定和变形很重要。本研究展示了功能性脂质如何用于调节囊泡-表面相互作用,并阐明了囊泡-底物相互作用在囊泡破裂中的作用。
相关推荐:
DSPE-PEG-PDP
DSPE-PEG-PEI
DSPE-PEG-PLA
DSPE-PEG-PLGA
DSPE-PEG-Progestrone
DSPE-PEG-RGD
DSPE-PEG-SC
DSPE-PEG-SCM
DSPE-PEG-SG
DSPE-PEG-SH
版权声明:
本平台根据相关科技期刊文献、教材以及网站编译整理的内容,仅用于对相关科学作品的介绍、评论以及课堂教学或科学研究。如有侵权,请联系我们删除。




 齐岳微信公众号
齐岳微信公众号 官方微信
官方微信 库存查询
库存查询